2. TCP message structure#
2.1. Main structure#
The structure of each packet is identical in both directions. The following scheme will be used for packet framing:
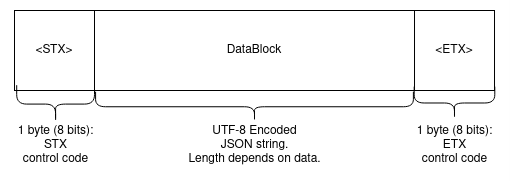
'\x02' and ends with <ETX> '\x03'.{"request": String(REQUESTED_TASK)}
{
"status": Boolean(Is the request understood and processed),
"response": OBJECT_REPRESENTING_RESULT
}
Properties and valid values of the data block
Property name |
Type |
Valid input or output |
|---|---|---|
request |
String |
Input: “GetState” / “SystemStart” / “SystemStop” / “StartLogging” / “StopLogging” / “TriggerImage” |
state |
Boolean |
Output: “true” / “false “ depending on the request’s acceptance or rejection |
response message |
Optional string |
Output: a free-text comment for debugging or logging |
2.2. Structure of the request data block#
{"request": String(REQUESTED_TASK)}
Valid values of “request”
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Get the current logging status |
|
Start the sensor system |
|
Stop the sensor system |
|
Start logging |
|
Stop logging |
|
Camera triggering control Important Always include all three parameters LineID, SegmentID and ImageID in this request! |
2.3. Structure of the response data block#
{
"status": Boolean(Is the request understood and processed),
"response": OBJECT_REPRESENTING_RESULT
}
The "status" in the response will be set to false if there is a syntax error, a failure in TCP packet framing, an unrecognized request, or any other communication-related error. This can occur only if the sent request is malformed or if there are errors or data loss/corruption during transmission.
If the packet framing fails, the server will not attempt to recover the communication on the current socket, as this could lead to undefined behavior. An error response will be sent, and the socket will be closed. TOPOFLIGHT should then reestablish the connection.
If an error occurs elsewhere (such as a JSON syntax error or an unrecognized command) and does not disrupt TCP packet framing, the response message will include the error. In this case, the socket will remain open, allowing communication to continue.
If the request is successfully parsed and recognized, the "status" in the response will be set to true.
The response will contain a "response" field, with its structure depending on the specific request that was sent.
2.4. Bad request response object structure#
When a request is not recognized, "response" will contain a descriptive message:
{
"message": String(free-text comment explaining why request was not possible to process)
}
2.5. “GetState” response#
When "GetState" is called, the "response" structure contains the following message:
{
"state": Integer(CURRENT_SYSTEM_STATE)
"message": Optional-String(free-text comment, for debugging/logging purposes)
}
Valid values of “state”
State ID |
State name |
|---|---|
|
“CONNECTED” |
|
“STARTING” |
|
“NOT_LOGGING” |
|
“LOGGING” |
|
“STOPPING” |
|
undefined and reserved for later use |
|
“ERROR” |
See states and state switches for a more detailed explanation.
The "message" field, if present, provides a more detailed explanation of the state. Currently, it is used only in the “ERROR” state, but it may be incorporated for other states in the future.
2.6. State switch response#
When "SystemStart", "SystemStop", "StartLogging" or "StopLogging" are called, "response" contains the following message:
{
"success": Boolean(depending on the request's acceptance or rejection),
"message": Optional-String(free-text comment for debugging/logging purposes)
}
The field “success” is
Boolean value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
when the request was accepted and is going to be performed. |
|
when for some reason the request was rejected and will not be performed. |
The "message" field is typically omitted when the request is successfully accepted. However, if the request is rejected, it will contain an explanation for the rejection.
2.7. Examples of full requests and their full responses#
Valid requests and example responses
-
Non-error state
Request:
{"request": "GetState"}Response:
{"status": true, "response": {"state": 2}}Explanation: State 2: Starting
-
Error state
Request:
{"request": "GetState"}Response:
{"status": true, "response": {"state": 10, "message": "Lidar storage full."}}Explanation: State 10: Error message: Lidar storage full
-
Successful request to switch state
Request:
{"request": "StartLogging"}Response:
{"status": true, "response": {"success": true}}Explanation: Start logging successful
-
Unsuccessful request to switch state
Request:
{"request": "StopLogging"}Response:
{"status": true, "response": {"success": false, "message": "Current State STARTING is not appropriate to perform StopLogging."}}Explanation: Stop logging not successful
Invalid and malformed requests
-
Undefined Request (“DoSomething”)
Request:
{"request": "DoSomething"}Response:
{"status": false, "response": {"message": "Task not recognized."}}Explanation: see valid requests
-
Undefined abbreviation (“req” instead of “request”)
Request:
{"req": "GetState"}Response:
{"status": false, "response": {"message": "Bad request structure"}} -
Missing brace
Request:
{"request": "GetState"Response:
{"status": false, "response": {"message": "JSON cannot be parsed."}}
Camera triggering requests
Request: {"request":"TriggerImage","LineID":[LineID],"SegmentID":[SegID],"ImageID":[ImgID]}
Response:
{"ImageState": 0, "LineID": [LineID], "SegmentID": [SegID], "ImageID": [ImgID]}
ImageState: 0 Error while triggering{"ImageState": 1, "LineID": [LineID], "SegmentID": [SegID], "ImageID": [ImgID]}
ImageState: 1 Trigger confirmation{"ImageState": 2, "LineID": [LineID], "SegmentID": [SegID], "ImageID": [ImgID]}
ImageState: 2 Stored successfully{"ImageState": 3, "LineID": [LineID], "SegmentID": [SegID], "ImageID": [ImgID]}
ImageState: 3 Error
