7. Queries#
Gain a deeper understanding of your flight plan by using the functions available in the Queries tab of the Navigation bar .
At the top of the Queries sidebar, select one of the buttons to open the corresponding panel that provides further interaction options.

Available tools (from left to right):
Measurement of distances and areas
Image position queries
Flight line queries
Sun elevation angle
The following section explains how to effectively apply these tools.
7.1. Measurement of distances and areas#
7.1.1. Distance measurement#
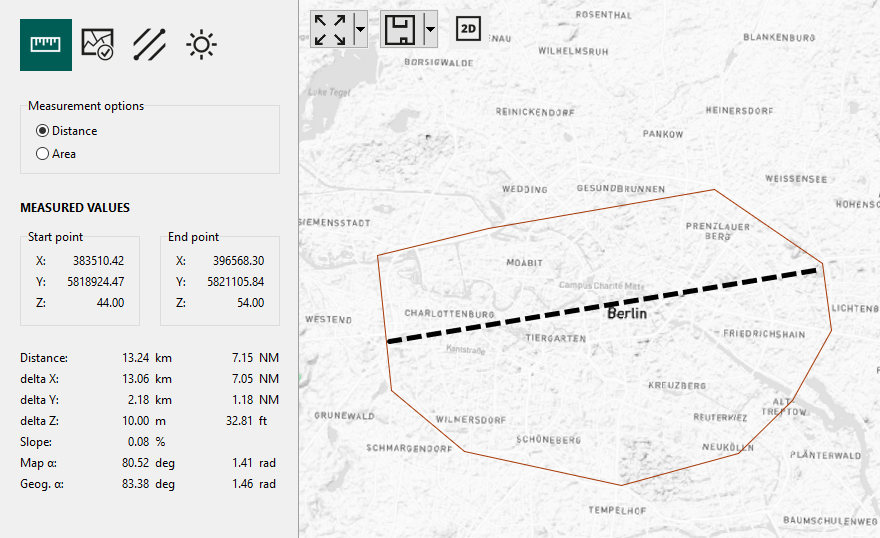
Determine the distance between two points on the map using the built-in measurement function. Utilize this feature not only to precisely measure distances but also to gain insights into height differentials and azimuth values for your planning and analysis needs.
Hint
In the secondary sidebar, you will also gain access to other valuable information, such as:
azimuth
coordinates of the start and end point
difference in height
slope
7.1.2. Area measurement#
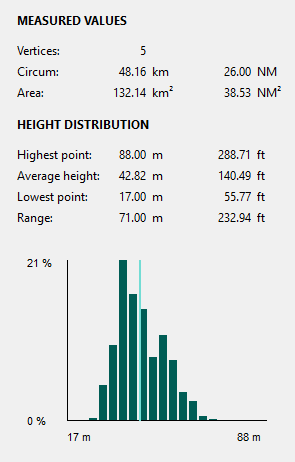
MISSIONPLANNER provides a useful tool to measure the extent of areas.
Hint
Move the vertices to make some fine adjustments to the polygon:
Click on the vertex you want to move. The vertex will become red.
Drag the vertex to its new destination.
The polygon with the dashed line and the measurement values are updated.
7.2. Image position queries#
The menu for image sequence queries offers different methods for the selection of image positions. At the bottom of the sidebar menu, there are several functions on how to proceed with the selection.
Selection method |
Result |
|---|---|
Rectangle |
Use the mouse drag to select an area with a rectangle bounding box in the map. |
Click on polygon |
Select an already defined area as reference for the spatial query. |
Attribute |
Define equations to make a query based on the properties of the shape. |
Image sequence |
Check the space between two image trigger points on the same flight line to ensure it adequately aligns with the camera capture rate limitation. |
7.2.1. Spatial queries#
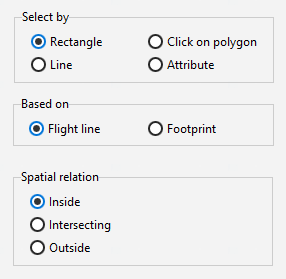
Spatial queries are made with the selection methods Rectangle and Click on polygon.
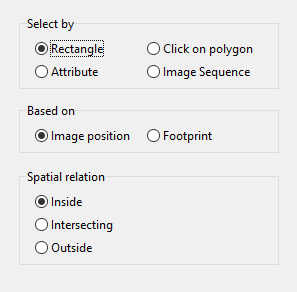
Select whether the function should be based on the Image position or its Footprint.
Choose the geographical context from the following options:
Inside: All image positions/footprints will be selected if the point or footprint is entirely inside the reference area. The shape will not be selected if it touches the reference area.
Intersecting: Image positions/footprints that fall within or touch the reference area will be selected.
Outside: Image positions/footprints that fall outside of or do not touch the reference area will be selected.
According to the selection method, you can then perform the query by using the mouse drag to select an area (method Rectangle) or by using an already defined area (method Click on polygon).
7.2.2. Properties queries#
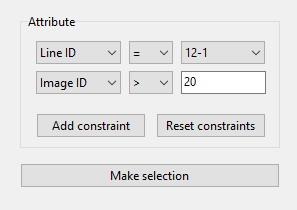
The Attribute selection method offers different selection criteria to build up a query.
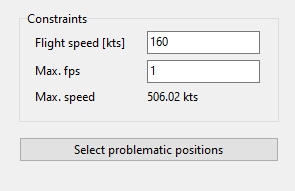
7.2.3. Image sequence queries#
This query is used to find locations at which the camera capture rate might be insufficient.
7.2.4. Making use of the selection#
Point selections can be used for the following purposes:
Deletion of areas with unwanted image points, e.g. where no pictures may be taken.
Shortening of flight lines.
Modification of flight lines in areas where image points do not meet your requirements.
Use the buttons on the bottom of the secondary sidebar to:
Unselect points
make an Inverse selection
Delete selected items
or Export selection to temporary layer, which will then appear in the layers panel.
Important
The deletion of data points cannot be undone! Only click on Delete selected items if you are completely certain that your selection is accurate.
If uncertain, it is advised to use the Save as option and save the project under a different name before proceeding to delete items. Automatic flight line recalculation for accidentally deleted image points is possible. Shortened flight lines, however, need to be fixed manually.
7.3. Flight line queries#
Flight line queries generally are performed analogous to image position queries. Here, a new selection method Line as well as the option based on Flight line are available. If select by Attribute is chosen, a larger variety of attribute options are given in the respective dropdown menu.
Selection method |
Result |
|---|---|
Rectangle |
Use the mouse drag to select an area with a rectangle bounding box in the map. |
Click on polygon |
Select an already defined area as reference for the spatial query. |
Attribute |
Define equations to make a query based on the properties of the shape. |
Line |
Select specific lines by clicking and then dragging the mouse (spatial relation inside not available). |
7.4. Know when to fly#
The sun’s elevation angle not only dictates the time window for the flight, spanning from sunrise to sunset, but it is also a crucial determinant for capturing high-quality images. During low sun angle degrees shadows become excessively long and thus reduce the image quality. Large sun angle degrees during mid-day can cause reflections, particularly from water bodies, that become overly intense, leading to potential issues like cross-fade. Therefore, knowing the optimal time window for the flight is essential for obtaining the best outcome.
